|
Abstract
Each of three adult New
Zealand rabbits, 2 male and 1 female albinos, was exposed dorsally or ventrally,
to 2450-MHz plane waves for 20 min under each of several field conditions: 1)
to continuous waves (CW) at 5
m W/cm²; 2) to pulsed waves (PW) of 1-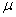 s width that recurred 700 pps at
an average of 5 m
W/cm²; and at a peak of 7.1 W/cm²; 3) to PW of 10-µs width at a peak of 13.7
W/cm²; that were synchronized with and triggered by the R wave of the
electrocardiogram (EKG) at various delay times (0, 100, and 200 ms; and 4) to
CW at 80 m
W/cm². Carbon-loaded Teflon electrodes were used to record the EKG from
forelimbs of an animal before, during, and after irradiation whilst it was
maintained in a constant exposure geometry in a
wooden squeeze box. Field induced changes in the heart-beat rate were
observed at 80 mW/cm² but not at lower average power densities, although a
weak positive chronotropic effect might have been
occasioned by PW introduced at 100 and 200 ms after the R wave peak. No
cumulative effect was observed over a period of four months. Thermographic analysis revealed relatively little
absorption of microwave energy by the myocardium irrespective of anatomical
aspect of exposure. s width that recurred 700 pps at
an average of 5 m
W/cm²; and at a peak of 7.1 W/cm²; 3) to PW of 10-µs width at a peak of 13.7
W/cm²; that were synchronized with and triggered by the R wave of the
electrocardiogram (EKG) at various delay times (0, 100, and 200 ms; and 4) to
CW at 80 m
W/cm². Carbon-loaded Teflon electrodes were used to record the EKG from
forelimbs of an animal before, during, and after irradiation whilst it was
maintained in a constant exposure geometry in a
wooden squeeze box. Field induced changes in the heart-beat rate were
observed at 80 mW/cm² but not at lower average power densities, although a
weak positive chronotropic effect might have been
occasioned by PW introduced at 100 and 200 ms after the R wave peak. No
cumulative effect was observed over a period of four months. Thermographic analysis revealed relatively little
absorption of microwave energy by the myocardium irrespective of anatomical
aspect of exposure.
|