|
Abstract
Silicon nitride requires the use
of susceptive additives for microwave liquid phase sintering due to the
material's low dielectric loss. In this article, we report the effect of
complex dielectric properties of two compositions of sintering aids on 2.45
GHz microwave sintered Si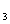 N N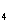 with respect to
power absorption, temperature distribution and densification behavior. The
temperature dependent dielectric properties were measured from 25°C to 1400°C using a
conventional cavity perturbation technique. Finite Difference Time Domain
(FDTD) electromagnetic simulations coupled with a thermal solver was used to
predict the microwave power absorption and the corresponding temperature
evolution inside the samples. The additive with higher dielectric loss (4 wt%
Mg0. 6 wt% Y with respect to
power absorption, temperature distribution and densification behavior. The
temperature dependent dielectric properties were measured from 25°C to 1400°C using a
conventional cavity perturbation technique. Finite Difference Time Domain
(FDTD) electromagnetic simulations coupled with a thermal solver was used to
predict the microwave power absorption and the corresponding temperature
evolution inside the samples. The additive with higher dielectric loss (4 wt%
Mg0. 6 wt% Y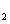 0 0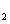 and 2.5 wt% Zr0 and 2.5 wt% Zr0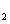 ) produces a greater sintered density than the lower loss
additive (4 wt% Mg0 and 6 wt% Y ) produces a greater sintered density than the lower loss
additive (4 wt% Mg0 and 6 wt% Y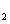 0 0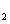 ) or pure Si ) or pure Si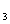 N N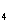 . Although microwave loss at temperatures below 600șC is
insignificant with or without the additives, the loss begins to increase at
higher temperatures when the additives are present and has a strong upward
trend above l000°C. Above 1200°C
the sample containing Zr0 . Although microwave loss at temperatures below 600șC is
insignificant with or without the additives, the loss begins to increase at
higher temperatures when the additives are present and has a strong upward
trend above l000°C. Above 1200°C
the sample containing Zr0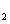 exhibited the
greatest loss. Numerical simulations at the peak sintering temperature show
greater microwave power absorption and higher temperature in the sample with
the highest loss additive. The simulation results correlate to the difference
in densification behavior observed. The simulation was also useful because
the material temperature was not accurately provided by optical pyrometer
measurements of the crucible sample holder. exhibited the
greatest loss. Numerical simulations at the peak sintering temperature show
greater microwave power absorption and higher temperature in the sample with
the highest loss additive. The simulation results correlate to the difference
in densification behavior observed. The simulation was also useful because
the material temperature was not accurately provided by optical pyrometer
measurements of the crucible sample holder.
Keywords:
Dielectric properties, microwave sintering, Silicon Nitride, FDTD
|