New paper accepted to Journal of Biomedical Optics
.
N. A. Turko, A. Peled, and N. T. Shaked, “Wide-field interferometric phase microscopy with molecular specificity using plasmonic nanoparticles,” Journal of Biomedical Optics, Vol. 18, No. 11, 111414:1-8, 2013.
.
Abstract: We present a method for adding molecular specificity to wide-field interferometric phase microscopy (IPM) by recording the phase signatures of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) labeling targets of interest in live cells. The AuNPs are excited by light at a wavelength corresponding to their absorption spectral peak, evoking a photothermal (PT) effect due to their plasmonic resonance. This effect induces a local temperature rise, resulting in local refractive index and phase changes that can be detected optically. Using a wide-field interferometric phase microscope, we acquired an image sequence of the AuNPs sample phase profile without requiring lateral scanning, and analyzed the time-dependent profile of the entire field of view using a Fourier analysis, creating a map of the locations of AuNPs in the sample. The system can image a wide-field PT phase signal from a cluster containing down to 16 isolated AuNPs. AuNPs were then conjugated to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibodies and inserted to an EGFR-overexpressing cancer cell culture, which was imaged using IPM, and verified by confocal microscopy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time wide-field interferometric PT imaging is performed at the subcellular level without the need for a total-internal-reflection effects or scanning.
.
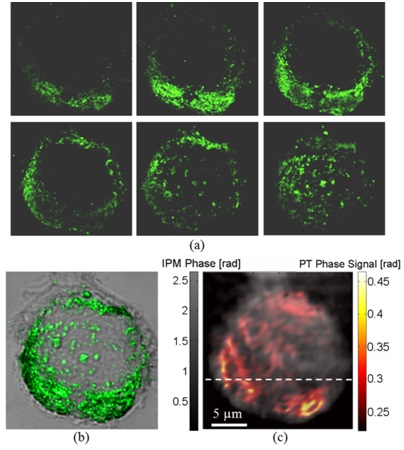 Imaging of MDA-MB 468 (EGFR+) cancer cell with conjugated AuNPs:
Imaging of MDA-MB 468 (EGFR+) cancer cell with conjugated AuNPs:
(a) Confocal imaging: Six consecutive confocal images of the AuNPs in the cell, from top-left image, representing the bottom of the cell, to bottom-right image, representing the top of the cell, in axial steps of 0.5 µm apart.
(b) Confocal plus DIC imaging: Cumulative confocal image of the AuNPs (colored), as obtained by summing the six consecutive confocal images shown in (a), overlaying a DIC image of the same cel (grayscale).
(c) PT IPM plus regular IPM imaging: PT phase image of the AuNPs (colored), overlaying a wide-field IPM phase image of the same cell (grayscale).
Figure is modified from Journal of Biomedical Optics [PDF].