Designing Design CoursesExemplified by a high school mechatronics courseEli Kolberg, Yoram Reich, Ilya Levin |
|
Hebrew Version
גרסה עברית |
|
|
|
Content:
2. Additional Related Information
3. Workshops for Educational Institutions
4. Presentations (1-2 hours long)
5. Publication
In this project we designed a mechatronics course for high school students. There are two unique aspects to this project that are not present in other design courses that we have encountered:
1. The design of the course used design methods that were either available or that we developed. This relates to our position on research methodology.
2.
The course design has been
implemented successfully in numerous schools in
1. Students improved their grades in science (mathematics, physics, and chemistry) in response to the new course design.
2. Students improved their perception of technology. Many of them selected to study engineering.
3. Students improved their design skills and resulting products. This has also been demonstrated by winning the first places an international robotics competition (see a video of 2005 winning robot).
A year after the comparative study (2004-5), the results of the program that could be observed (e.g., superior design performance exemplified by winning the international robotics competition and improved perception of technology) are even better than before.
Extended statistics confirm that the method continues to work and lead to outstanding performance in student achievements including winning in Robocup competitions.
The course design and its results would easily satisfy ABET accreditation criteria for engineering programs even though our course is a high school course.
This project is a part and a demonstration of a research motto in which theory, practice, and education intimately interact. More specifically, the study follows two steps: course design and course implementation and reflection. The following loop shows the factors that play a role in these steps and their interactions.
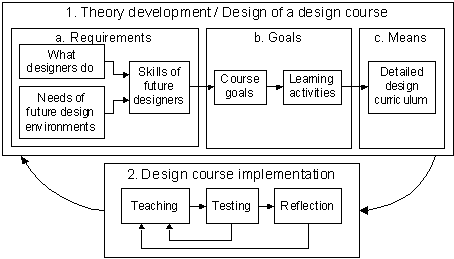
Related Projects include:
- RQFD a design method used to place priorities over parts of the curriculum.
- SOS a design method that will be taught in the future and that would be used to configure design courses for different educational settings.
- Learning control using dual representations.
Additional Related Information:
- www.robotica.co.il
- Robotic contests
Workshops for Educational Institutions:
1. email Yoram Reich (yoram @ eng.tau.ac.il )
Presentations (1-2 hours long):
1.
Designing contexts for learning design
Publications:
1.
E. Kolberg, Y. Reich, and I. Levin, Project-based
high school mechatronics course, International Journal of Engineering
Education, 19(4):557562, 2003.
2.
I. Levin,
3.
I. Levin, E. Kolberg, and
Y. Reich, Designing control system for mobile educational robot, INFO
International Journal on Informatics in Education, 3:8794, 2004. (Invited
paper, in Russian).
4.
Y. Reich, E. Kolberg, and I. Levin, Designing contexts for learning
design, in Proceedings of Mudd
Design Workshop V, Harvey Mudd College, CA, 2005.
5.
E. Kolberg, Y. Reich, and I. Levin, Transforming design education
by design, in Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on
Design Theory and Methodology (DTM), (New York, NY), ASME, 2005.
6.
Y. Reich,
7.
Y. Reich,
8. E. Kolberg, Y. Reich, and I. Levin, Designing design methodologies for robotics products, First Israeli Conference on Robotics, 2006.
9.
10. E. Kolberg, Y. Reich, and I. Levin, Express engineering change management, in CDROM Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Engineering Design (ICED), The Design Society, 2007.
11.
E. Kolberg, Y. Reich, and I. Levin, Design of design methodology for
autonomous robots, CD proceedings of the RoboCup
Symposium 2007,
12. E. Kolberg, Y. Reich, and I. Levin, Design methodology for mobile robots, presented at The 9th Bar-Ilan Symposium on the Foundations of Artificial Intelligence (BISFAI 2007), Bar-Ilan University, Ramat Gan, Israel, 2007.
Videos / Pictures:
Last
modified: 6/3/2007 1:59:00 PM